All about bed bug bites with key solutions to truly get rid of them!

All about bed bug bites with key solutions to truly get rid of them!
All about bed bug bites with key solutions to truly get rid of them!
A small parasitic insect called a bed bug primarily feeds on the blood of warm-blooded humans and animals. Here is an overview of this insect:
Identification
- The scientific name is: Cimex lectularius (most common in temperate regions) and Cimex hemipterus (most common in tropical regions).
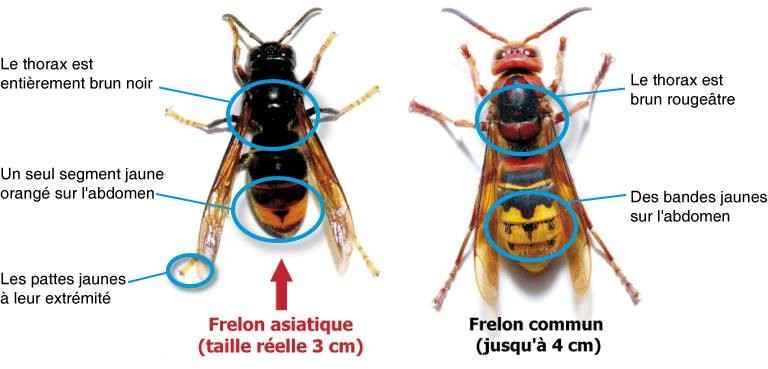
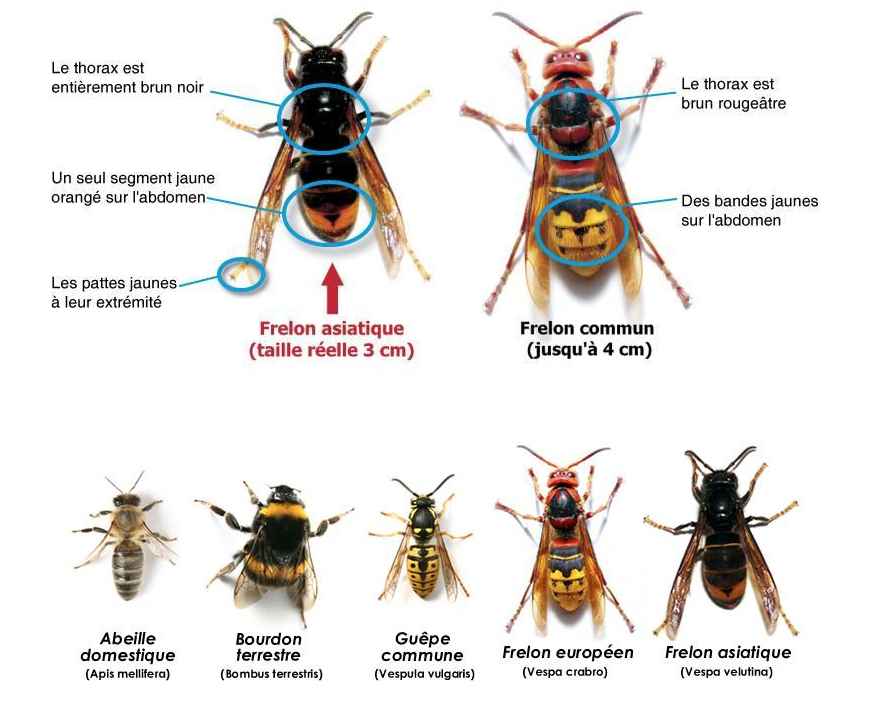
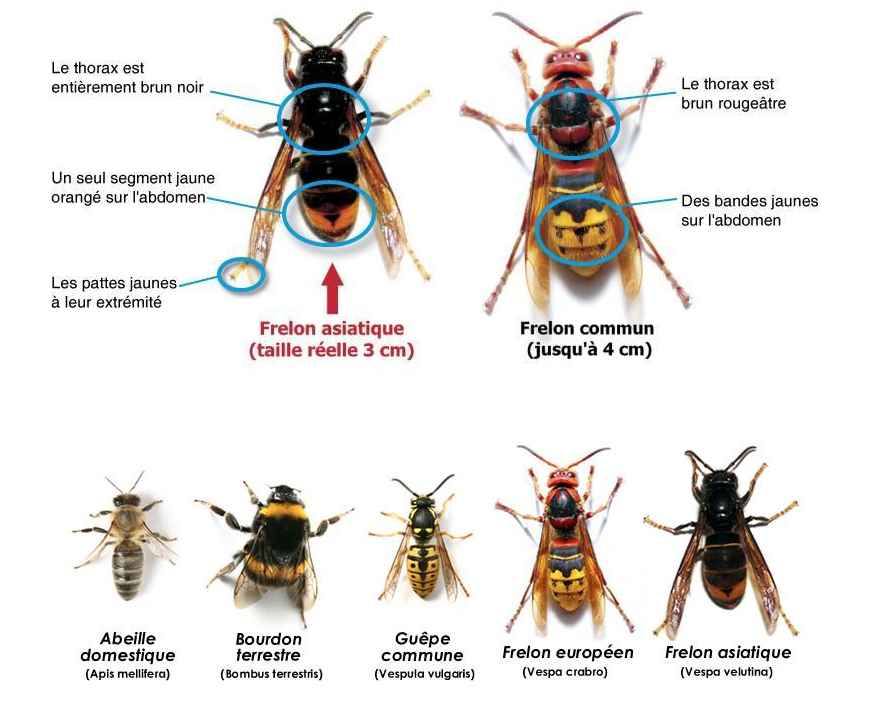
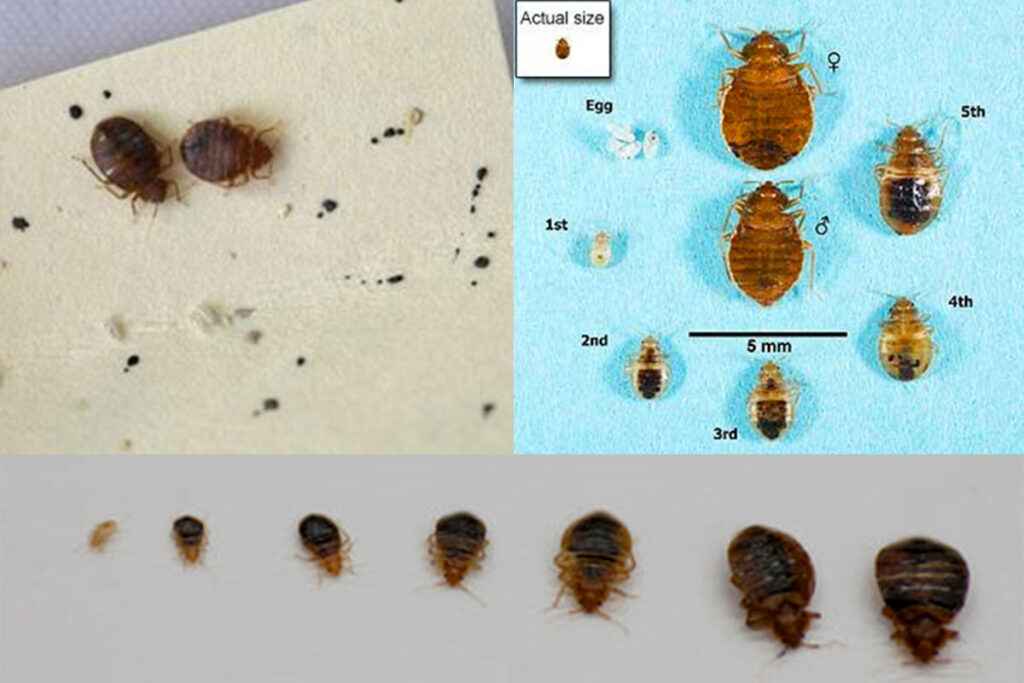
- Appearance: Adults are oval-shaped, reddish-brown in color, and measure about 5 to 7 mm long. Their bodies can become red and swollen after feeding on blood.
- Eggs: They are white and oval-shaped, measuring about 1 mm long. They are often hidden in cracks or crevices, making them difficult to spot.
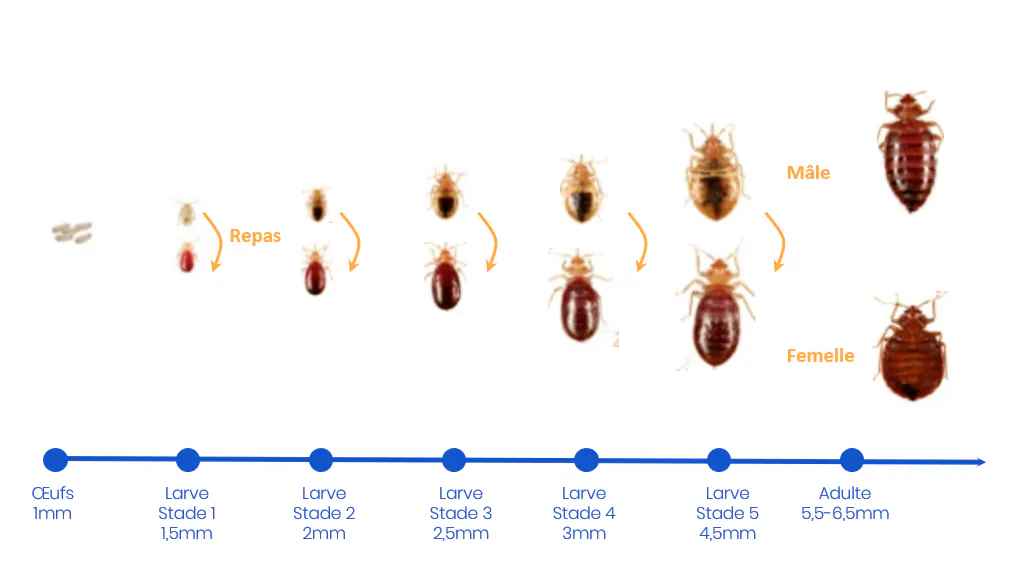
What does a bed bug look like?
Eggs
- Color: Off-white.
- Size: About 1 mm in length, barely visible to the naked eye.
- Shape: Oval and elongated.
Nymphs (Young bed bugs)
- Color: Transparent after hatching, gradually becoming redder as they feed on blood.
- Size: Start at about 1.5 mm in length and grow to adult size of 5 to 7 mm through several molts.
- Shape: Oval and flattened, resembling adults but smaller.
Adults
- Color: Reddish-brown, becoming redder after feeding on blood.
- Size: About 5 to 7 mm in length, roughly the size of an apple seed.
- Shape: Oval body, laterally flattened, allowing the insect to squeeze into very narrow spaces.
- Other features: Adults have short antennae, small eyes, and well-developed legs that allow them to move quickly. They do not have wings and therefore cannot fly.

Life Cycle
- Egg: Bed bugs start their life as eggs, which hatch after about 10 days.
- Nymphs: They go through five developmental stages (nymphs), requiring a blood meal to move from one stage to another, a process that can last from 5 weeks to several months, depending on environmental conditions.
- Adult: Once mature, bed bugs can live for about 10 months or more under certain conditions.
Behavior and Habits
- Feeding: Generally, they feed at night, but they can adapt to their host's sleep cycle. A bed bug can feed for 5 to 10 minutes before hiding in its hiding place.
- Hideouts: They prefer to hide near their food source (humans) and can be found in mattresses, box springs, bed frames, behind wallpapers, or even in electrical outlets and electronic devices.
Signs of Infestation
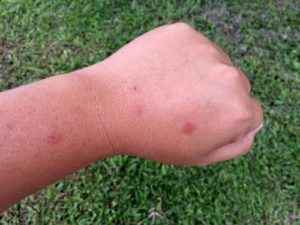
- Bites: Often the first indication, these bites appear as red bumps, often in lines or clusters, and can cause itching.
- Traces: Small black spots (excrement) on sheets, mattresses, and bedding, as well as exuviae (shed skins) of nymphs.
- Odor: Severe infestation can produce a sweet odor due to pheromones released by bed bugs.
Transmission
Although they do not fly or jump, bed bugs can move quickly on surfaces. They are frequently transported in luggage, furniture, clothing, or any other moved object.
How to Recognize a Bed Bug Bite?
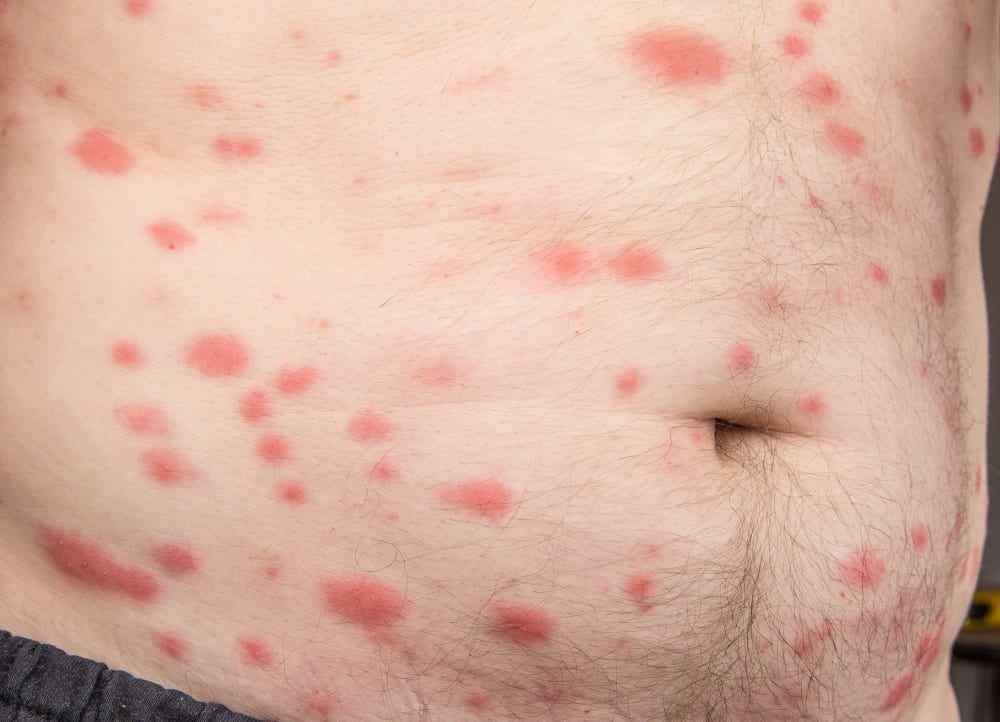
Appearance of Bites
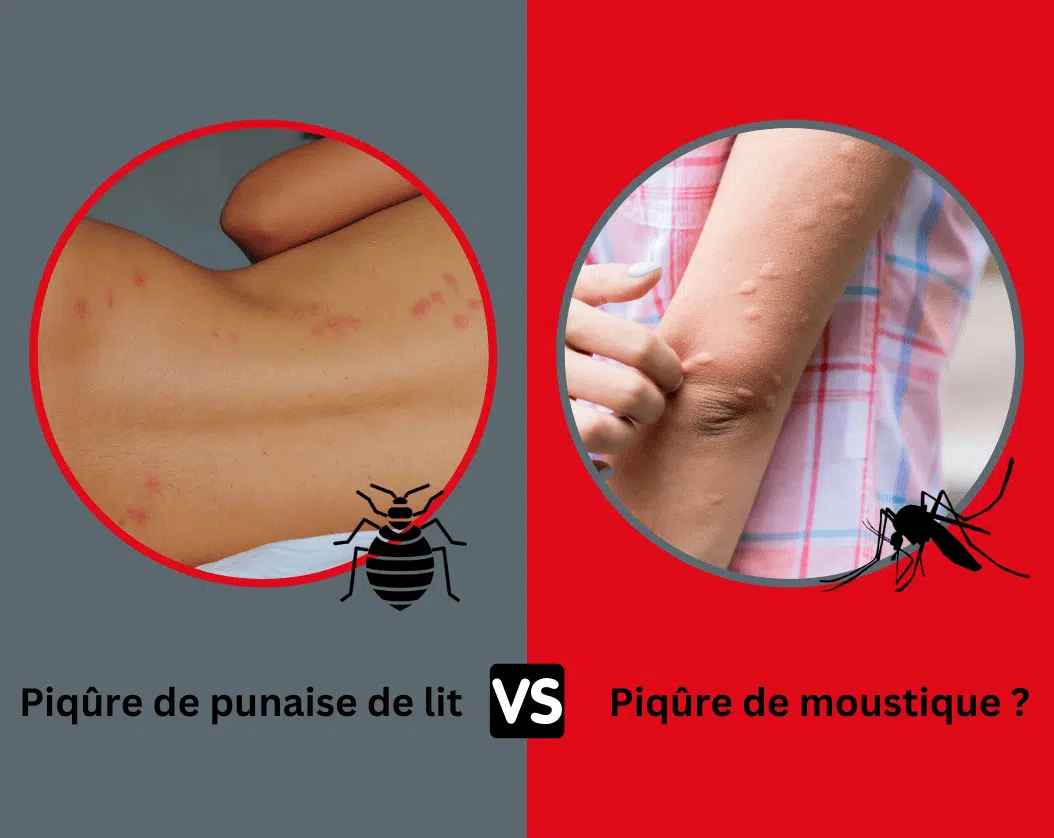
- Size: Bites are generally small, about 1 to 5 mm in length.
- Shape: Bites often have the appearance of slightly swollen red bumps, resembling mosquito bites.
- Arrangement: They often occur in lines or groups of three or more, sometimes known as "breakfast, lunch, and dinner." The reason for this arrangement lies in the behavior of the bed bug, which bites repeatedly while moving.
Symptoms
- Itching: Bed bug bites often cause itching, which can be intense and uncomfortable.
- Skin Reaction: A person's reaction to a bed bug bite can vary. Some people may be allergic, while others may not be.
Difference from Other Bites
- Mosquito bites: They are usually isolated and found more all over the body.
- Flea bites: Often concentrated around the legs or ankles.
- Allergic reactions: Insect bites may resemble rashes, but they are usually accompanied by other symptoms, such as hives.
What are the Prevention Methods?
There are many methods to try to prevent bed bug infestation from entering and spreading in your environment.
Here are some different approaches.
Although there are no specific pharmaceutical products to eliminate bed bugs from your home, some items can help prevent or detect them earlier:
At Home
- Reduce clutter to limit potential hiding places for bed bugs.
- Use bed bug-proof mattress and box spring covers to prevent bed bugs from entering or exiting.
- Regularly vacuum floors, furniture, mattresses, and bed frames to eliminate bed bugs and their eggs.
- Mattress anti-dust mite covers: these covers are mainly marketed for dust mites, but they can also protect you from bed bugs.
- Adhesive tapes or traps: the presence of bed bugs can be detected using certain types of traps.
Regular Inspections
- Regularly check mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and other furniture for signs of infestation such as bed bugs themselves, small black spots (their excrement), shed skins, or eggs.
- Inspect cracks and hidden areas with a magnifying glass and flashlight if necessary.
During Travel
- Before settling in, check hotel rooms or any other accommodation for signs of bed bugs.
- Avoid placing your luggage directly on the floor or bed by using luggage racks.
- During your stay, keep your clothes in airtight bags.
- Before returning, check your luggage and clothes.
When Buying Secondhand Furniture or Clothing
- Carefully inspect secondhand furniture, mattresses, and clothing before bringing them home.
- Immediately wash secondhand clothing in hot water and dry them at high temperature.
General Precautions
Be cautious when hosting guests in your home or sharing living spaces such as dormitories or apartments.
How to Treat This Phenomenon? I'm Infested with Bed Bugs.
Treatment Area Preparation
- Reduce clutter to limit bed bug hiding places and facilitate treatment.
- Wash clothes, bedding, and curtains in hot water (at least 60°C) and dry them at high temperature for at least 30 minutes.
- Wrap non-washable items in plastic bags and place them in the freezer for at least 72 hours, or use heat treatment bags if available.
2 Different Treatment Methods

Chemical Treatment
- Insecticides: Bed bugs can be effectively eliminated using specific insecticides. These include sprays, powders, fumigators, and aerosols.
Non-Chemical Treatment
- Heat: At temperatures above 45°C, bed bugs and their eggs die. The use of heat chambers or hot steam can be an effective method.
- Cold: Bed bugs can be killed if infested items are exposed to temperatures below -18°C for at least 72 hours.
- Vacuuming: You can reduce the number of bed bugs and eggs by carefully vacuuming infested areas. Be sure to place the vacuum bag in a sealed plastic bag and dispose of it outside immediately.
Bricomachin advises you to mix both methods to enhance the desired result. It is also recommended to put your clothes in an airtight bag and put insecticide in it. If you can also pass these same clothes through a dryer at 60 degrees, it is also recommended but it will depend on whether your clothes can withstand such a temperature for a minimum of 30 minutes.
Follow-up and Maintenance
- Conduct regular inspections and treatments as needed. Due to their ability to hide and survive long periods without food, a single intervention often does not eliminate all bed bugs.
- Keep an eye out for any reinfestation, especially in the weeks following treatment.
How much does a bed bug treatment cost?
The price varies depending on the area to be treated, but generally ranges between 200Euros and 1500Euros. This price includes a minimum of 2 visits.
Are there treatments available at pharmacies?
The eradication of bed bugs should not be accomplished through a person-focused strategy but through a habitat-based strategy. This is why no medicinal treatment can be sold in pharmacies. Thus, bed bugs will not be killed in the surroundings, but only on your body. However, pharmacies can provide bed bug products and advice for controlling bites while reducing the risk of infestation in your home.
Regarding bed bug bites:

- Anti-itch creams: Creams containing hydrocortisone or other anti-inflammatory components can reduce itching.
- Oral antihistamines: Can help relieve allergic reactions and itching.
- Soothing lotions: Lotions containing calamine or aloe can provide relief.
Bed Bugs in France? A Real Problem?
In France, like in many other countries, bed bugs are a growing problem. In France, there is an increase in bed bug infestations due to several reasons, such as increased travel abroad, exchanges of secondhand furniture and clothing, as well as increased resistance of these insects to parasitic treatments. Here are some important points to consider regarding the bed bug situation in France:
- Large cities and tourist areas are particularly affected due to population density and high volume of travelers. Paris, for example, has reported a growing number of infestation cases in recent years.
- Infestations are not limited to residential accommodations; they can affect hotels, hostels, student accommodations, and even some public transports.
In France, health authorities and professional organizations have intensified their awareness campaign on the bed bug problem. Information campaigns aim to raise awareness about detecting bed bugs, preventing their spread, and effectively treating infestations. Individuals and professionals can find and manage bed bug infestations using online guides and resources.


 Francais
Francais